ShellCheck一个用于Shell脚本的静态分析工具
ShellCheck - Shell 脚本静态分析工具
ShellCheck 是一款 GPLv3 工具,可为 bash/sh shell 脚本提供警告和建议:
ShellCheck 的目标是:
-
指出并澄清初学者常见的语法问题,这些问题会导致 shell
给出难以理解的错误信息。 -
指出并澄清典型的中级语义问题,这些问题会导致 shell
行为异常且违反直觉。 -
指出可能导致高级用户原本可以正常工作的脚本在未来情况下失败的细微警告、极端情况和陷阱。
请参阅错误代码库,了解 ShellCheck 可以帮助您识别的示例!
使用方法
ShellCheck 有多种使用方法!
在线
将 ShellCheck 脚本粘贴到 https://www.shellcheck.net 即可获得即时反馈。
ShellCheck.net 始终与最新的 git 提交同步,是体验 ShellCheck 最简单的方法。推荐给你的朋友!
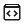
从终端
在终端中运行 shellcheck yourscript 即可获得即时输出,如上所示。
在编辑器中
你可以在各种编辑器中直接查看 ShellCheck 的建议。
-
Sublime,通过 SublimeLinter。
-
Pulsar Edit(原 Atom),通过 linter-shellcheck-pulsar。
-
VSCode,通过 vscode-shellcheck。
-
大多数其他编辑器,通过 GCC 错误兼容性。
在您的构建或测试套件中
虽然 ShellCheck 主要面向交互式使用,但它也可以轻松添加到构建或测试套件中。
它规范地使用退出代码,因此您只需在流程中添加 shellcheck 命令即可。
例如,在 Makefile 中:
check-scripts:
# 如果以下任何文件出现警告,则运行失败
shellcheck myscripts/*.sh或在 Travis CI .travis.yml 文件中:
script:
# 如果以下任何文件出现警告,则运行失败
- shellcheck myscripts/*.shInstalling
在本地安装 ShellCheck 最简单的方法是通过您的包管理器。
On systems with Cabal (installs to ~/.cabal/bin):
cabal update
cabal install ShellCheckOn systems with Stack (installs to ~/.local/bin):
stack update
stack install ShellCheckOn Debian based distros:
sudo apt install shellcheckOn Arch Linux based distros:
pacman -S shellcheck或者从 AUR 获取无依赖项的 shellcheck-bin。
On Gentoo based distros:
emerge --ask shellcheckOn EPEL based distros:
sudo yum -y install epel-release
sudo yum install ShellCheckOn Fedora based distros:
dnf install ShellCheckOn FreeBSD:
pkg install hs-ShellCheckOn macOS (OS X) with Homebrew:
brew install shellcheckOr with MacPorts:
sudo port install shellcheckOn OpenBSD:
pkg_add shellcheckOn openSUSE
zypper in ShellCheckOr use OneClickInstall - https://software.opensuse.org/package/ShellCheck
On Solus:
eopkg install shellcheckOn Windows (via chocolatey):
C:\> choco install shellcheckOr Windows (via winget):
C:\> winget install --id koalaman.shellcheckOr Windows (via scoop):
C:\> scoop install shellcheckFrom conda-forge:
conda install -c conda-forge shellcheckFrom Snap Store:
snap install --channel=edge shellcheckFrom Docker Hub:
docker run --rm -v "$PWD:/mnt" koalaman/shellcheck:stable myscript
# Or :v0.4.7 for that version, or :latest for daily builds或者,如果您想要一个更大的基于 Alpine Linux 的镜像来扩展,请使用 koalaman/shellcheck-alpine。它的工作方式与常规 Alpine 镜像完全相同,但预装了 shellcheck。
Using the nix package manager:
nix-env -iA nixpkgs.shellcheckUsing the Flox package manager
flox install shellcheck或者,您可以在此处下载最新版本的预编译二进制文件:
- Linux,x86_64(静态链接)
- Linux,armv6hf,例如 Raspberry Pi(静态链接)
- Linux,aarch64,又称 ARM64(静态链接)
- macOS, aarch64
- macOS, x86_64
- Windows, x86
或查看 GitHub 版本 获取其他版本
(包括 最新 元版本,用于每日 git 构建)。
目前 Apple Silicon 尚无官方二进制文件,但第三方构建版本可通过
ShellCheck for Visual Studio Code 获取。
发行版软件包已附带“man”页面。如果您从源代码构建,可以使用以下命令安装:
pandoc -s -f markdown-smart -t man shellcheck.1.md -o shellcheck.1
sudo mv shellcheck.1 /usr/share/man/man1pre-commit
要通过 pre-commit 运行 ShellCheck,请将以下钩子添加到您的 .pre-commit-config.yaml 中:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/koalaman/shellcheck-precommit
rev: v0.7.2
hooks:
- id: shellcheck
# args: ["--severity=warning"] # 可选,仅显示错误和警告Travis CI
Travis CI 现在已默认集成 ShellCheck,因此您无需手动安装。
如果您仍然想这样做,以便随时升级或确保您使用的是
最新版本,请按照以下步骤安装二进制版本。
安装预编译二进制文件
预编译二进制文件以 tar.xz 文件的形式提供。要解压它们,请确保
xz 已安装。
在 Debian/Ubuntu/Mint 上,您可以使用 apt install xz-utils。
在 Redhat/Fedora/CentOS 上,请使用 yum -y install xz。
简单的安装程序可能会执行如下操作:
scversion="stable" # 或 "v0.4.7",或 "latest"
wget -qO- "https://github.com/koalaman/shellcheck/releases/download/${scversion?}/shellcheck-${scversion?}.linux.x86_64.tar.xz" | tar -xJv
cp "shellcheck-${scversion}/shellcheck" /usr/bin/
shellcheck --version从源代码编译
本节介绍如何从源代码目录构建 ShellCheck。ShellCheck 使用 Haskell 编写,编译需要 2GB 内存。
安装 Cabal
ShellCheck 使用 Cabal 构建和打包。请使用系统的包管理器(例如使用 apt-get、brew、emerge、yum 或 zypper)安装包“cabal-install”。
在 macOS (OS X) 上,您可以使用 brew 快速安装 Cabal,只需几分钟,而如果尝试从源代码编译,则需要 30 多分钟。
$ brew install cabal-install
在 MacPorts 上,该软件包的名称为“hs-cabal-install”,而原生 Windows 用户应从 https://www.haskell.org/platform/ 安装最新版本的 Haskell 平台。
验证“cabal”是否已安装,并使用以下命令更新其依赖项列表:
$ cabal update
编译 ShellCheck
使用“git clone”命令克隆此仓库,然后“cd”到 ShellCheck 源目录进行构建/安装:
$ cabal install
这将编译 ShellCheck 并将其安装到您的“~/.cabal/bin”目录中。
将此目录添加到您的“PATH”中(对于 bash,请将此目录添加到您的“~/.bashrc”中):
export PATH="$HOME/.cabal/bin:$PATH"注销并重新登录,并验证您的 PATH 是否设置正确:
$ which shellcheck
~/.cabal/bin/shellcheck在原生 Windows 系统中,“PATH”应该已经设置好了,但系统可能使用的是旧版代码页。在“cmd.exe”、“powershell.exe”和 Powershell ISE 中,请确保使用 TrueType 字体,而不是 Raster 字体,并使用“chcp”将活动代码页设置为 UTF-8 (65001):
chcp 65001在 Powershell ISE 中,您可能需要额外更新输出编码:
[Console]::OutputEncoding = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8运行测试
要运行单元测试套件:
$ cabal test
错误代码库
那么 ShellCheck 会查找哪些内容呢?以下是检测到的问题的不完整列表。
引用
ShellCheck 可以识别几种类型的错误引用:
echo $1 # Unquoted variables
find . -name *.ogg # Unquoted find/grep patterns
rm "~/my file.txt" # Quoted tilde expansion
v='--verbose="true"'; cmd $v # Literal quotes in variables
for f in "*.ogg" # Incorrectly quoted 'for' loops
touch $@ # Unquoted $@
echo 'Don't forget to restart!' # Singlequote closed by apostrophe
echo 'Don\'t try this at home' # Attempting to escape ' in ''
echo 'Path is $PATH' # Variables in single quotes
trap "echo Took ${SECONDS}s" 0 # Prematurely expanded trap
unset var[i] # Array index treated as glob条件语句
ShellCheck 可以识别多种类型的错误测试语句。
[[ n != 0 ]] # Constant test expressions
[[ -e *.mpg ]] # Existence checks of globs
[[ $foo==0 ]] # Always true due to missing spaces
[[ -n "$foo " ]] # Always true due to literals
[[ $foo =~ "fo+" ]] # Quoted regex in =~
[ foo =~ re ] # Unsupported [ ] operators
[ $1 -eq "shellcheck" ] # Numerical comparison of strings
[ $n && $m ] # && in [ .. ]
[ grep -q foo file ] # Command without $(..)
[[ "$$file" == *.jpg ]] # Comparisons that can't succeed
(( 1 -lt 2 )) # Using test operators in ((..))
[ x ] & [ y ] | [ z ] # Accidental backgrounding and piping经常被误用的命令
ShellCheck 可以识别命令使用不当的情况:
grep '*foo*' file # Globs in regex contexts
find . -exec foo {} && bar {} \; # Prematurely terminated find -exec
sudo echo 'Var=42' > /etc/profile # Redirecting sudo
time --format=%s sleep 10 # Passing time(1) flags to time builtin
while read h; do ssh "$h" uptime # Commands eating while loop input
alias archive='mv $1 /backup' # Defining aliases with arguments
tr -cd '[a-zA-Z0-9]' # [] around ranges in tr
exec foo; echo "Done!" # Misused 'exec'
find -name \*.bak -o -name \*~ -delete # Implicit precedence in find
# find . -exec foo > bar \; # Redirections in find
f() { whoami; }; sudo f # External use of internal functions初学者常犯的错误
ShellCheck 可以识别许多常见的初学者语法错误:
var = 42 # Spaces around = in assignments
$foo=42 # $ in assignments
for $var in *; do ... # $ in for loop variables
var$n="Hello" # Wrong indirect assignment
echo ${var$n} # Wrong indirect reference
var=(1, 2, 3) # Comma separated arrays
array=( [index] = value ) # Incorrect index initialization
echo $var[14] # Missing {} in array references
echo "Argument 10 is $10" # Positional parameter misreference
if $(myfunction); then ..; fi # Wrapping commands in $()
else if othercondition; then .. # Using 'else if'
f; f() { echo "hello world; } # Using function before definition
[ false ] # 'false' being true
if ( -f file ) # Using (..) instead of test
风格
ShellCheck 可以提出改进风格的建议:
[[ -z $(find /tmp | grep mpg) ]] # Use grep -q instead
a >> log; b >> log; c >> log # Use a redirection block instead
echo "The time is `date`" # Use $() instead
cd dir; process *; cd ..; # Use subshells instead
echo $[1+2] # Use standard $((..)) instead of old $[]
echo $(($RANDOM % 6)) # Don't use $ on variables in $((..))
echo "$(date)" # Useless use of echo
cat file | grep foo # Useless use of cat数据和输入错误
ShellCheck 可以识别与数据和输入相关的问题:
args="$@" # Assigning arrays to strings
files=(foo bar); echo "$files" # Referencing arrays as strings
declare -A arr=(foo bar) # Associative arrays without index
printf "%s\n" "Arguments: $@." # Concatenating strings and arrays
[[ $# > 2 ]] # Comparing numbers as strings
var=World; echo "Hello " var # Unused lowercase variables
echo "Hello $name" # Unassigned lowercase variables
cmd | read bar; echo $bar # Assignments in subshells
cat foo | cp bar # Piping to commands that don't read
printf '%s: %s\n' foo # Mismatches in printf argument count
eval "${array[@]}" # Lost word boundaries in array eval
for i in "${x[@]}"; do ${x[$i]} # Using array value as key鲁棒性
ShellCheck 可以提出提高脚本稳健性的建议:
rm -rf "$STEAMROOT/"* # Catastrophic rm
touch ./-l; ls * # Globs that could become options
find . -exec sh -c 'a && b {}' \; # Find -exec shell injection
printf "Hello $name" # Variables in printf format
for f in $(ls *.txt); do # Iterating over ls output
export MYVAR=$(cmd) # Masked exit codes
case $version in 2.*) :;; 2.6.*) # Shadowed case branches可移植性
ShellCheck 会在使用 shebang 不支持的功能时发出警告。例如,如果你将 shebang 设置为 #!/bin/sh,ShellCheck 会发出类似于 checkbashisms 的可移植性问题警告:
echo {1..$n} # Works in ksh, but not bash/dash/sh
echo {1..10} # Works in ksh and bash, but not dash/sh
echo -n 42 # Works in ksh, bash and dash, undefined in sh
expr match str regex # Unportable alias for `expr str : regex`
trap 'exit 42' sigint # Unportable signal spec
cmd &> file # Unportable redirection operator
read foo < /dev/tcp/host/22 # Unportable intercepted files
foo-bar() { ..; } # Undefined/unsupported function name
[ $UID = 0 ] # Variable undefined in dash/sh
local var=value # local is undefined in sh
time sleep 1 | sleep 5 # Undefined uses of 'time'各种各样的
ShellCheck 还发现了一系列其他问题:
PS1='\e[0;32m\$\e[0m ' # PS1 colors not in \[..\]
PATH="$PATH:~/bin" # Literal tilde in $PATH
rm “file” # Unicode quotes
echo "Hello world" # Carriage return / DOS line endings
echo hello \ # Trailing spaces after \
var=42 echo $var # Expansion of inlined environment
!# bin/bash -x -e # Common shebang errors
echo $((n/180*100)) # Unnecessary loss of precision
ls *[:digit:].txt # Bad character class globs
sed 's/foo/bar/' file > file # Redirecting to input
var2=$var2 # Variable assigned to itself
[ x$var = xval ] # Antiquated x-comparisons
ls() { ls -l "$@"; } # Infinitely recursive wrapper
alias ls='ls -l'; ls foo # Alias used before it takes effect
for x; do for x; do # Nested loop uses same variable
while getopts "a" f; do case $f in "b") # Unhandled getopts flags忽略问题
可以通过环境变量、命令行、单独或全局文件忽略问题:
https://github.com/koalaman/shellcheck/wiki/Ignore
报告错误
如有任何错误或功能建议,请使用 GitHub 问题跟踪器:
https://github.com/koalaman/shellcheck/issues
贡献
请以 GitHub 拉取请求的形式提交代码或文档的补丁!查看 ShellCheck Wiki 上的 DevGuide。
贡献内容必须遵循 GNU GPLv3 许可证。
贡献者保留版权。
版权
ShellCheck 遵循 GNU 通用公共许可证 v3 许可证。此许可证的副本包含在 LICENSE 文件中。
版权所有 2012-2019,Vidar 'koala_man' Holen 和贡献者。
祝您 ShellCheck 愉快!